Chain Signatures by NEAR Protocol: Enhancing Blockchain Interoperability
Discover how NEAR Protocol's Chain Signatures revolutionize blockchain interoperability by enabling secure, cross-chain transactions on a single account
Introduction
NEAR Protocol recently launched Chain Signatures, a cross-chain interoperability feature on its mainnet. Chain Signatures enable user accounts and smart contracts to securely sign and execute transactions across multiple blockchains.
Chain Signatures are a major contribution to chain abstraction in the Web3 space. Chain abstraction aims to deliver a seamless user experience by abstracting away the blockchain technology, ensuring that account holders use blockchain-based applications without realizing they are on a blockchain.
Chain Signatures utilizes a decentralized Multi-Party Computation (MPC) network that enables NEAR accounts to create joint signatures from arbitrary payloads from the client, allowing NEAR users to control external blockchain accounts.
How Chain Signatures Work
- The Request is initiated by the Client
When a NEAR account needs to interact with a different blockchain, it first initiates the foreign transaction by calling the sign method of the MPC smart contract(v1.signer) to sign the transaction.
The v1.signer API is used by NEAR accounts to sign transactions when interacting with the blockchain, ensuring that they are securely authorized by the appropriate private key holders.
- MPC Service receives the Request and generates the Signature
The MPC service comprises a group of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) nodes run by validators that securely authorize transactions. Once they receive the request, the nodes collaboratively sign the transaction using their unique key fragments without sharing their private key information. Afterwards, the signatures are combined into a complete valid signature, and is returned to the NEAR blockchain
- The Signature relayed to the Destination
When the signature is ready, the client reconstructs the signed transaction using the signature and broadcasts it to the destination blockchain.
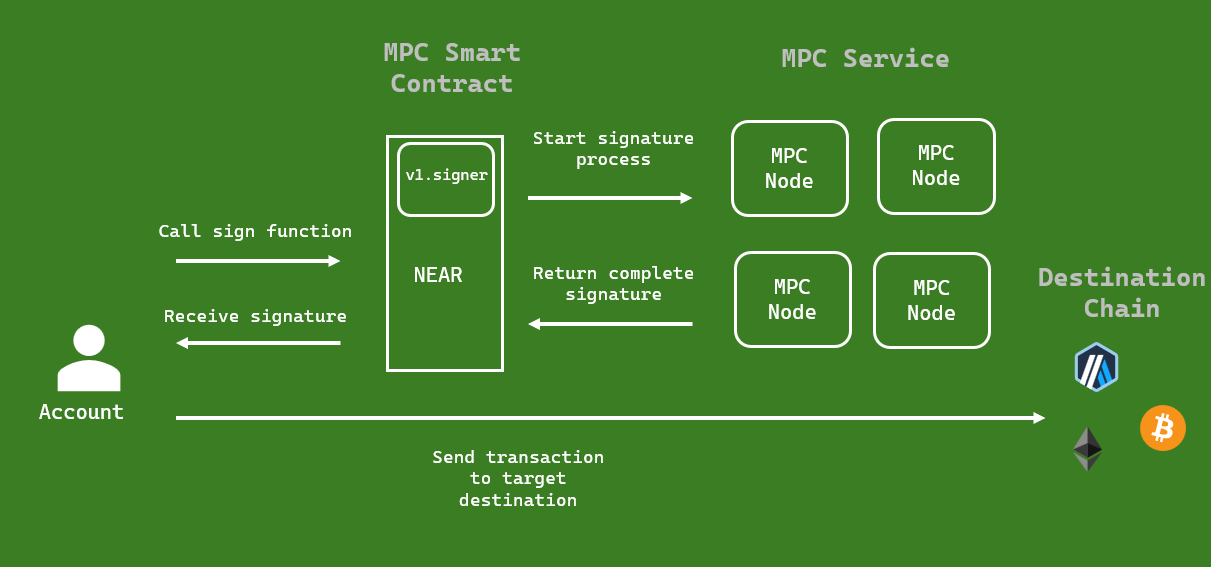
Figure 1: Representation illustrating how Chain Signatures function
This process is simplified for NEAR accounts, making navigating interactions across chains through one user interface easier without the complexity of managing wallets or dealing with bridging mechanisms. This paves the way for opportunities in chain lending, trading, and other financial operations.
Chain Signatures have already gained traction and are being used by a number of DeFi and Digital wallet companies. Some of the Chain Signatures dApps already active on mainnet include Defuse, a multichain spot DEX, as well as HERE Wallet and Sweat Wallet.
By eliminating the need for bridges, Chain Signatures can significantly expand the liquidity and utility of assets across various blockchains. This allows NEARs Chain Signatures smart contracts to participate in finance activities across blockchains without traditional bridging methods.
Unlike existing bridges or cross-chain messaging protocols which often struggle with scaling and comprehensive blockchain support, Chain Signatures can support multiple blockchains without native integration, whether Ethereum, Bitcoin or the Cosmos ecosystem.
Practical Uses of Chain Signatures
Inter-blockchain asset Swaps: Facilitate smooth asset exchanges between networks, enabling users to transfer assets without intricate bridging procedures.
DeFi Integration with Bitcoin: Enables NEAR contracts to participate in finance activities on blockchains like the Bitcoin network, that do not traditionally support smart contracts.
Multi Chain Account Abstraction: Simplifies user interactions with decentralized applications by abstracting the complexities of chain transactions.
Conclusion
Chain Signatures is opening new avenues for multi-chain applications, DeFi integration, and seamless user interactions by enabling contracts to authorize non-custodial transactions across multiple blockchains. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to expand, innovations like Chain Signatures are important for creating an interconnected and user-centric environment.
For more information on how Chain Signatures can enhance your blockchain projects, explore the Chain Signatures documentation.